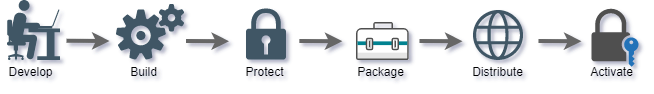
Develop
Application development process.
Build
Build release version of application from source code.
Protect
Protect application with PC Guard. This step can be automated with command line interface.
Package
Digitally sign protected application and package it into distribution setup (.exe, .msi or .zip)
Distribute
Distribute packaged application to end users by any means (Internet, CD, DVD, USB drive...)
Activate
Activate and lock protected application with activation code.
Standard protection
Standard protection is always applied to application during protection process regardless of selected protection method and it includes:
(application is wrapped into security envelope)
(application is encrypted)
(special anti-debugging code is embedded into protected application)
(application can not be decompiled)
Protection methods
There are four basic protection methods: PLAIN, REMOTE, NETWORK and USB and here is how they are related to standard protection:
Standard protection
Standard protection + Machine locking + Activation
Standard protection + Network licensing
Standard protection + USB locking
Protect any application
PC Guard protection is applied directly to compiled applications and modules by wrapping them into security envelope. This means that almost any kind of native (unmanaged) Windows, .NET framework, Windows .NET Core, standard and non-standard applications application can be protected regardless of programming language used.
Compatibility
Protected applications will run on latest 32-bit and 64-bit desktop and server Windows operating systems. Protected applications can be run from any storage device like hard drive, usb drive or directly from read-only storage like cd or dvd.
Out-of-the-box solution
By default, no additional programming and source code editing is required. PC Guard can by used by anyone, from absolute beginners to professional software developers. Protection process is simple and effective. Set project settings accordingly to your requirements and click on Protect! button to encrypt application. That's it!
Application is encrypted during protection process and our protection code is embedded into it. Security envelope consist of large number of encryption layers and anti-debugging, anti-reverse engineering code and contains all protection functions.
Protection code will gain control on startup, check license status, demo limitations, application integrity, initialize required data, decrypt protected application and pass control to it without dumping decrypted code to hard drive at any time.
Machine locking
Machine locking is the process of locking (linking) protected application to remote computer in order to prevent illegal usage on multiple computers. There are seven different locking parameters (locks) that can be enabled or disabled. Two of these are software locks (HD ID, OS ID) and five are hardware (HD ID (HW), CD/DVD, NET ID, CPU ID and BIOS ID) locks.
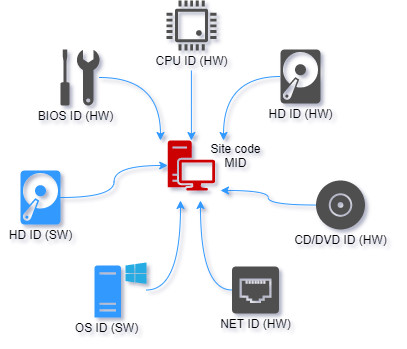
Site/MID codes are based on enabled locks and application signature value. Application signature uniquely identifies project files and thus protected application on remote computer.
Each lock can be marked as mandatory. If lock is marked as mandatory and if protection code is not able to obtain such lock on remote computer appropriate error message will be displayed to end user.
By default, change in any of selected locks will result in license reset. Application will erase current license, change site/mid codes and request new activation code. This default behavior can be customized with flexible licensing feature. If 'Changeable' flag is not selected, protection code will not allow changes for appropriate locking parameter. This is default behavior. If selected, protection code will allow changes for locking parameter.
If multiple hardware locking parameters are marked as changeable, protection code will not reset license as long as total number of changes is lower than defined maximum number of allowed hardware changes.
Use Machine ID decoding feature (in activation panel) to obtain each lock value from remote computer. In this way you can easily compare old and new locking parameters and thus prevent false requests for new activation codes.
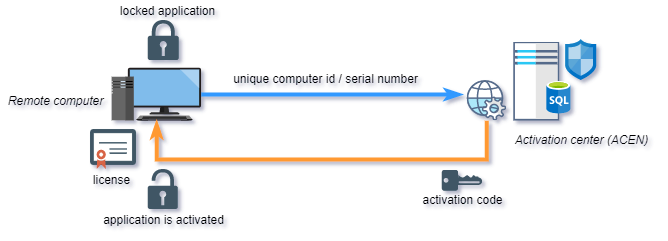
Activation
Effective machine locking requires software activation process. Software activation represents exchange of keys (activation codes) between you and your end users.
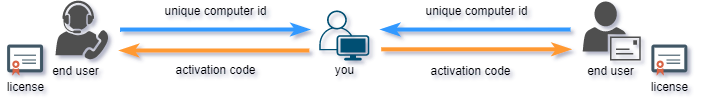
End user would submit his Site/MID codes (unique computer id) to you and you would provide appropriate valid activation code based on these codes back to end user. User can than activate his application on remote computer with provided activation code. If moved to another computer, protected application will generate different Site/MID codes and require new (different) activation code.
By default, Internet connection is not required for activation. Protected application can be securely activated even by phone, fax or e-mail. Activation process can also be fully automated with the help of Activation center: