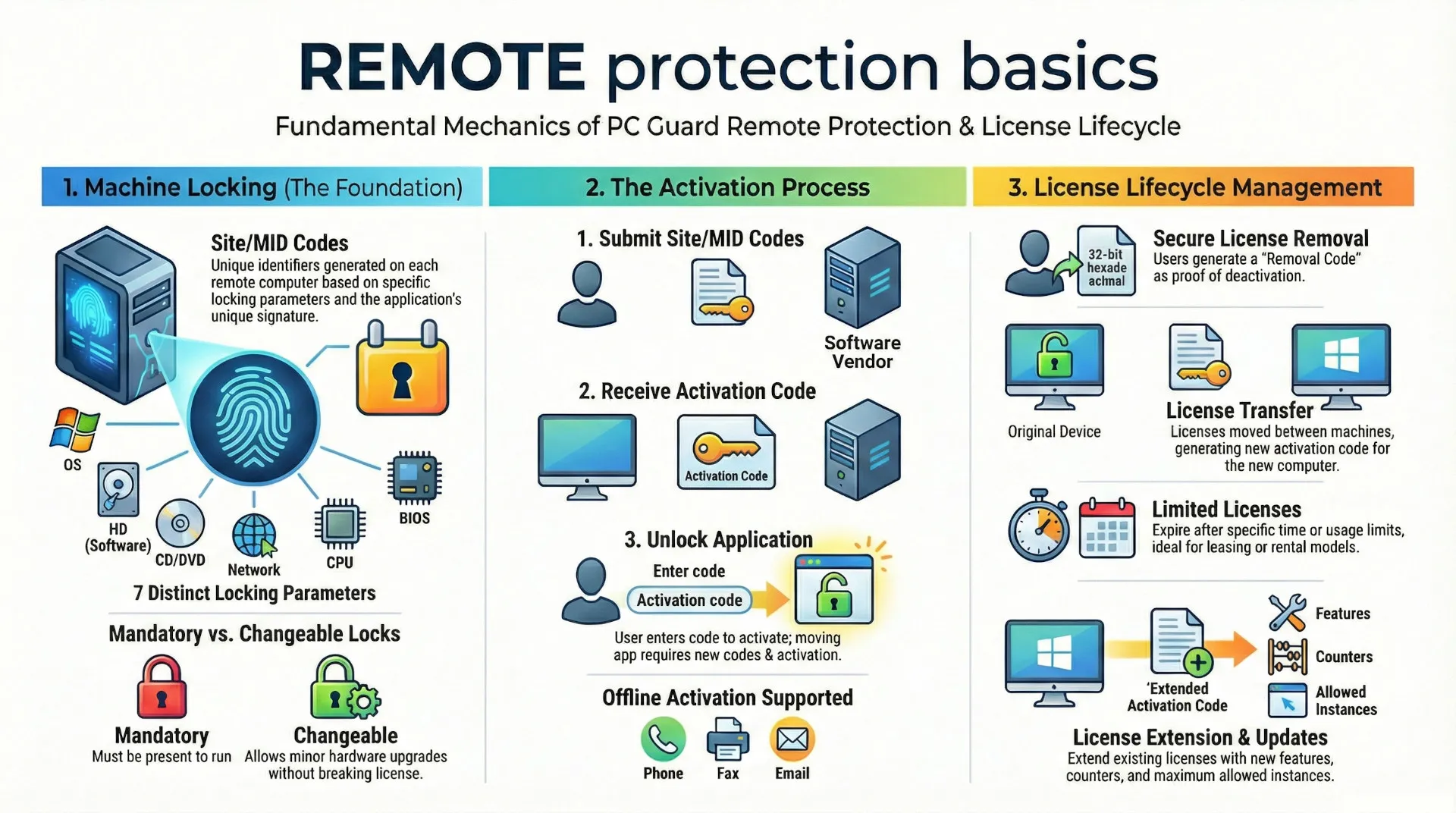
PC Guard's REMOTE protection feature allows you to securely lock your application to specific remote computers. This is crucial for software licensing, ensuring your software runs only on authorized machines.
How Remote Protection Works
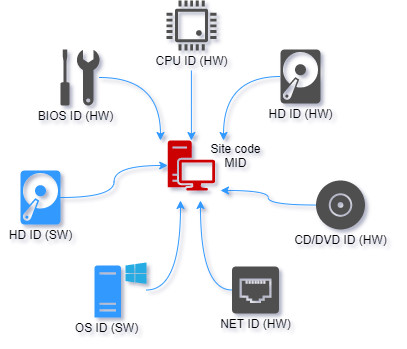
When your protected application runs on an end-user's computer, it generates a unique Site Code and Machine Identification (MID) Code. These codes are based on a combination of software and hardware parameters of that specific machine, along with a unique signature from your protected application.
To activate the software, the end-user provides you with these unique codes. You then use the PC Guard Control Panel (or an automated Activation Center) to generate a corresponding Activation Code. The user enters this Activation Code into their application, which then unlocks and runs.
Key Concepts & Components
Machine Locking Parameters: These are the unique identifiers from the remote computer that PC Guard uses to generate the Site/MID codes. You can select which ones to use for a robust locking mechanism.
Software Locks:
- HD ID: Hard Drive ID.
- OS ID: Operating System ID.
Hardware Locks:
- HD ID (HW): Hardware Hard Drive ID.
- CD/DVD: CD/DVD drive ID.
- NET ID: Network Adapter (MAC) ID.
- CPU ID: Processor ID.
- BIOS ID: Basic Input/Output System ID. You can mark any of these as mandatory. If a mandatory lock changes on the end-user's machine, the license may be reset, requiring re-activation.
Activation Dialog Box: This is the interface displayed by your protected application on the end-user's machine. It presents the Site/MID codes and allows the user to input the Activation Code.
PC Guard Control Panel: This is the tool you use as the developer to generate Activation Codes based on the Site/MID codes provided by your users.
Activation Center: An optional automated system for handling activation requests, removing the need for manual code exchange.
Understanding License Types & Management
Remote protection supports various license types and management features:
Demo Mode: You can set up your application to run in a trial (demo) mode for a specified period (e.g., number of days, runs, or minutes) before requiring full activation.
License Removal: You can remotely remove an existing license from a user's computer. This might be used if a user no longer needs the software or if there's suspicious activity.
License Transfer: Allows a user to transfer their license from one computer to another, typically by deactivating on the old machine and reactivating on the new one.
Limited Licenses: Ideal for rented or leased software, these licenses expire after a certain period or number of uses.
License Extension: Enables you to update or extend specific features, counters, or limitations of an existing license without requiring a full re-activation. This is useful for upgrades or adding new modules.
Implementing Remote Protection (General Steps)
While the detailed implementation steps are within the PC Guard software itself, here's a general workflow:
Protect Your Application: Use the PC Guard software to protect your application, configuring the desired remote protection settings. This includes selecting the machine locking parameters you want to enforce.
Distribute Protected Application: Provide the protected version of your software to your end-users.
User Attempts to Run: When a user tries to run the application for the first time, or if their license is reset due to hardware changes, the activation dialog box will appear, displaying their unique Site/MID codes.
Exchange Codes:
Manual: The user sends you their Site/MID codes (e.g., via email or phone). You use the PC Guard Control Panel to generate an Activation Code and send it back to them.
User Activates: The user enters the received Activation Code into the activation dialog, unlocking the software.
Automated: The user interacts with your Activation Center, which automatically generates and provides the Activation Code.
Conclusion
By leveraging these features, PC Guard allows you to implement robust licensing and protection for your software applications across various remote environments.