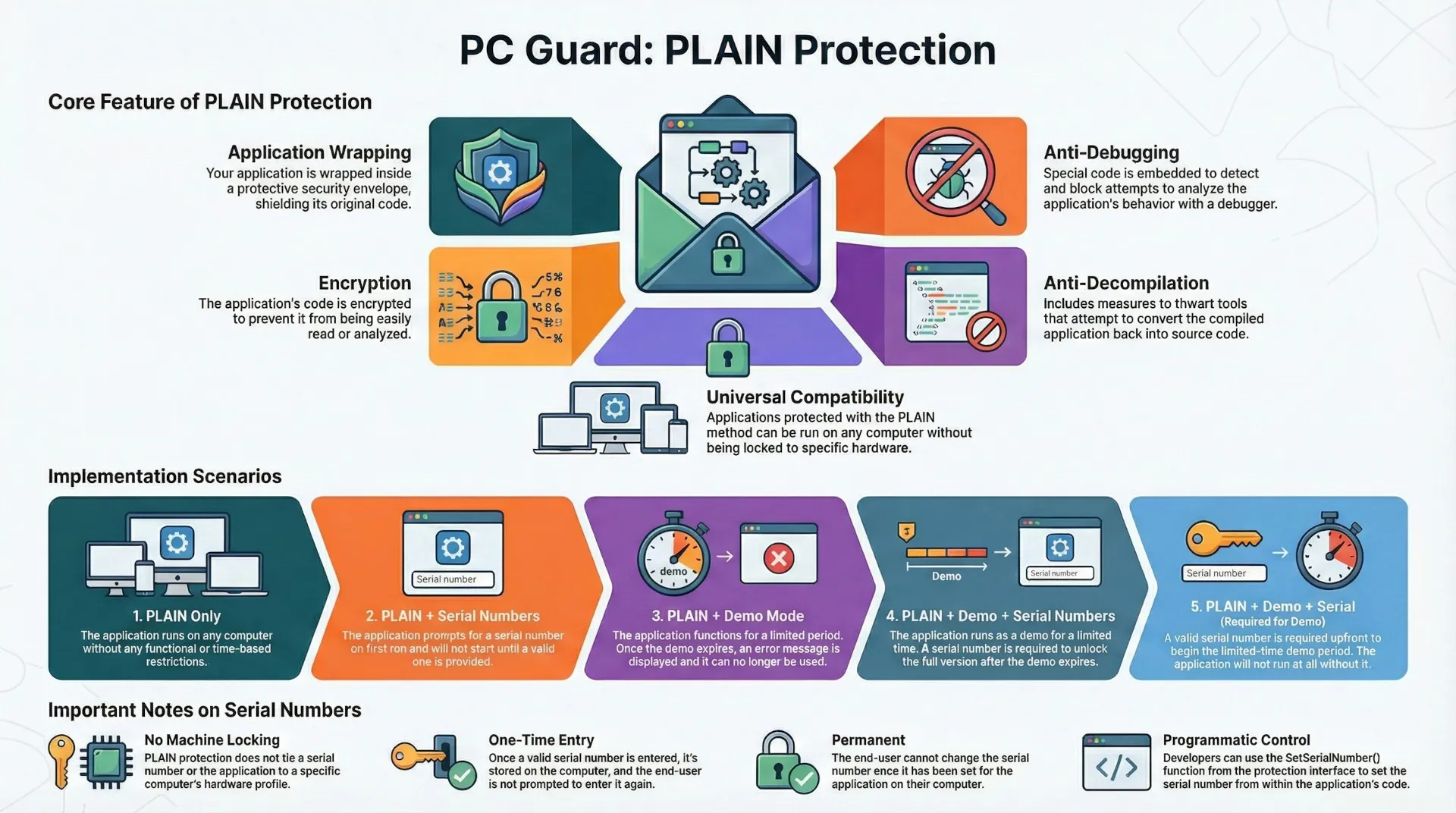
PLAIN protection is a foundational software security method designed to protect applications from reverse-engineering, patching, disassembly, and analysis. It achieves this by wrapping the application in a security envelope, encrypting its code, and embedding anti-debugging and anti-decompilation measures. A key characteristic of this method is its portability; an application protected with PLAIN protection can run on any computer without being locked to specific hardware.
This protection method can be implemented in several ways, either as a standalone measure or combined with licensing features like demo mode and serial numbers. These combinations create flexible distribution models, from unrestricted use to trial versions that require a serial number for full functionality. A critical limitation to note is the absence of machine locking, meaning the protection does not tie the application to a specific computer.
Core Features of PLAIN Protection
PLAIN protection is described as the most basic protection method, incorporating several key security techniques to safeguard software applications.
- Wrapping: The application is enclosed within a security envelope, which acts as a protective layer.
- Encryption: The application's code is encrypted, making it unreadable without the proper decryption key.
- Anti-Debugging: Specialized code is embedded into the protected application to detect and prevent debugging attempts.
- Anti-Decompilation: Measures are included to protect the application against decompilation tools.
Applications secured solely with PLAIN protection are designed to be fully portable and can be executed on any computer without restrictions.
Implementation Scenarios
PLAIN protection can be configured in five primary scenarios, offering different levels of access control and licensing models.
1. PLAIN
In its simplest form, the application is protected against reverse-engineering but is otherwise fully functional. It will work on any computer without any usage restrictions, time limits, or licensing requirements.
2. PLAIN + SERIAL NUMBERS
This scenario introduces basic licensing.
- The application will prompt the user for a serial number upon first launch.
- It cannot be run until a valid serial number is provided.
- Once a valid serial number is entered, the application runs without any further restrictions.
3. PLAIN + DEMO
This configuration creates a time-limited trial version of the application.
- The application will function for a predetermined limited period.
- After the demo mode expires, an error message is displayed, and the application will no longer run.
4. PLAIN + DEMO + SERIAL NUMBERS
This model provides a "try-before-you-buy" experience where users can convert a demo into a full version.
- The application initially runs in a demo mode for a limited period.
- A serial number is mandatory to continue using the application after the demo period expires.
- The user can provide a serial number at any point, either during the demo period or after it has expired.
- Once a valid serial number is supplied, the application is fully unlocked and operates without restrictions.
- Special Condition: If the "Display execution limitation counter" or "Display date limitation counter" options are also enabled, the application will display an activation dialog on every launch until a valid serial number is entered.
5. PLAIN + DEMO + SERIAL NUMBERS + SN is required for demo mode
This is a more restrictive trial model that requires user registration to begin the demo period.
- The application will prompt for a serial number at the outset and cannot be run, even in demo mode, until a valid serial is provided.
- Once the serial number is validated, the application enters a demo mode and will work for a limited period.
- When the demo period expires, an appropriate error message is displayed.
Operational Notes and System Behavior
The following notes describe the system's behavior, particularly concerning the use of serial numbers with PLAIN protection.
| Feature | Description |
| Serial Number Storage | Once a valid serial number is entered by the end user, it is stored on the computer. The user will not be prompted to enter it again. |
| Activation Dialog | After a valid serial number has been provided, the application will no longer display the activation dialog on startup. |
| Serial Number Immutability | The serial number cannot be changed by the end user once it has been set. |
| Programmatic Access | The SetSerialNumber() protection interface function can be used to set the serial number from within the protected application itself. |
| Data Retrieval | The serial number's value and the status of any custom features embedded within it can be obtained via the protection interface. |
| No Machine Locking | A crucial characteristic of the PLAIN protection method is the absence of machine locking. The license is not tied to a specific computer's hardware. |